Table of contents
In today’s world, where electricity is an essential part of our daily lives, inverters play a crucial role in ensuring uninterrupted power supply. Whether you are looking to harness solar energy or need a backup power source for your home, understanding the different types of inverters is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various types of inverters and their applications, helping you make an informed decision for your specific power needs.
Importance of Inverters in Various Applications
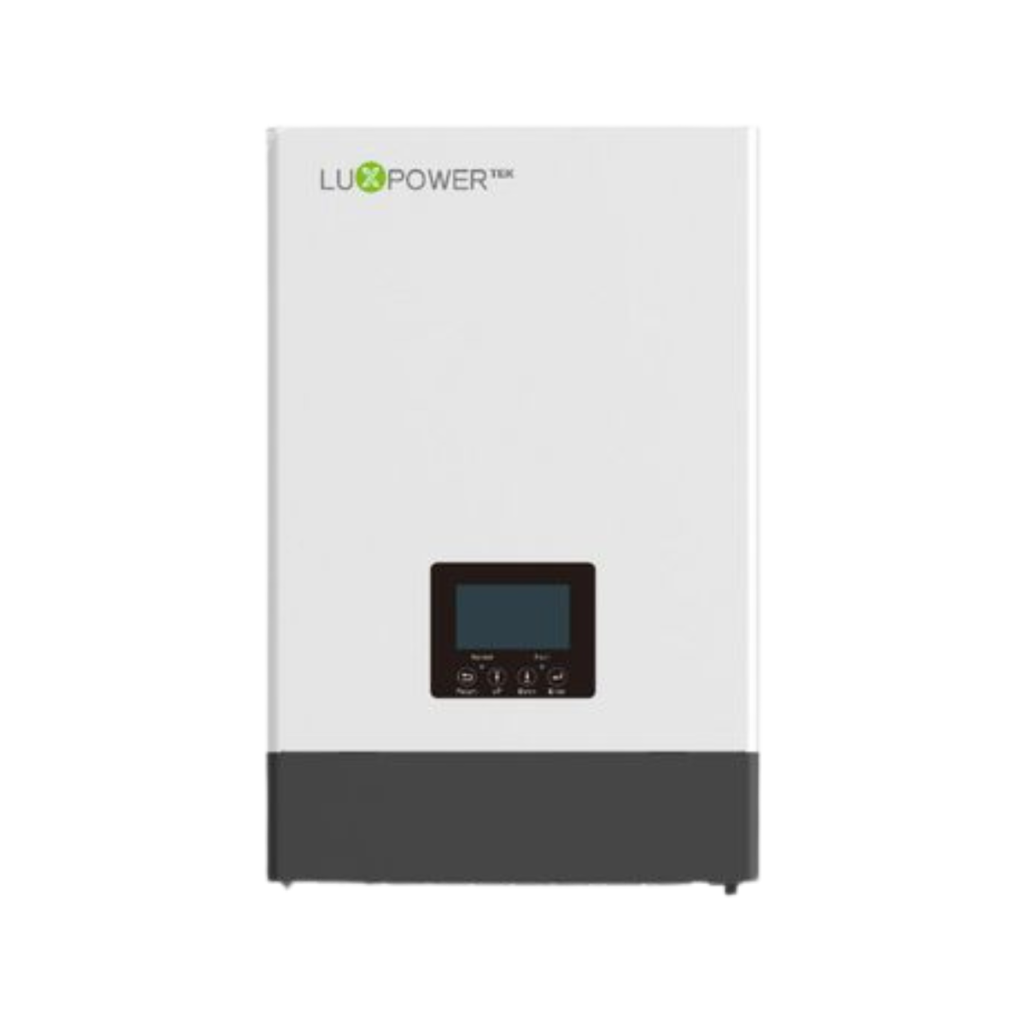
Inverters are devices that convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), allowing you to use DC power sources like batteries or solar panels to power appliances that require AC power. They are indispensable in various applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
In the residential sector, inverters are used to power home appliances during power outages. They provide a reliable backup power source, ensuring that you can continue with your daily activities even when the grid fails. In commercial and industrial sectors, inverters are used to power critical equipment, such as servers, telecommunications systems, and manufacturing machinery. They ensure uninterrupted operation, preventing costly downtime and potential losses.
Different Types of Inverters
Off-grid Inverters for Solar Energy Systems
Solar energy systems have gained popularity in recent years due to their environmental benefits and cost savings. Off-grid inverters are specifically designed for such systems, where the electricity generated from solar panels is stored in batteries for later use. These inverters convert the DC power from the batteries into AC power, which can be used to run appliances in your home or business.
Off-grid inverters come in various sizes and power capacities to accommodate different energy needs. They are equipped with advanced features such as maximum power point tracking (MPPT) to optimise the energy conversion process and ensure maximum efficiency. When choosing an off-grid inverter, consider factors such as the size of your solar energy system, the appliances you want to power, and the battery capacity required.
Grid-tied Inverters for Solar Energy Systems
Grid-tied inverters are another type of inverter commonly used in solar energy systems. Unlike off-grid inverters, grid-tied inverters do not require batteries for energy storage. Instead, they are connected directly to the electrical grid, allowing you to sell excess power back to the utility company through a process called net metering.
Grid-tied inverters work by synchronising the AC power generated by the solar panels with the utility grid’s AC power. This means that you can use the electricity generated by your solar energy system to power your home or business, while any excess power is fed back into the grid. This not only reduces your dependence on the utility company but also allows you to earn credits for the excess power you produce.
Hybrid Inverters for Solar Energy Systems
Hybrid inverters combine the best features of both off-grid and grid-tied inverters, making them a versatile choice for solar energy systems. These inverters allow you to store excess power in batteries for later use, similar to off-grid inverters. However, they also have the capability to synchronise with the utility grid, enabling you to sell excess power back to the grid.
The advantage of hybrid inverters is that they provide you with the flexibility to switch between grid-tied and off-grid modes, depending on your energy needs. This means that you can use the grid as a backup power source when your solar energy system cannot meet the demand, or you can rely solely on your solar panels and batteries to power your home or business during grid outages.
Stand-alone Inverters for Home Use
Stand-alone inverters are commonly used in homes where there is no access to the electrical grid. These inverters convert DC power from batteries, generators, or other renewable energy sources into AC power for everyday use. They are particularly useful in remote areas or during outdoor activities such as camping, where grid power is unavailable.
Stand-alone inverters come in different sizes and power capacities to suit various needs. They are designed to be portable and easy to install, allowing you to set up a power source wherever you need it. When choosing a stand-alone inverter, consider factors such as the power requirements of your appliances, the battery capacity, and the input voltage of your power source.
Modified Sine Wave Inverters
Modified sine wave inverters produce an AC waveform that approximates a sine wave through a series of steps. While the output is less smooth than a pure sine wave, these inverters are a cost-effective and straightforward choice for various applications. However, they may not be suitable for sensitive electronic equipment due to their less refined waveform.
Pure Sine Wave Inverters
Pure sine wave inverters generate an AC output waveform closely resembling a perfect sine wave. Ideal for powering sensitive electronic equipment requiring high-quality power, these inverters provide a smooth and continuous output. Although more complex and expensive than modified sine wave inverters, they are the preferred choice for critical applications.
Single-Phase Inverters
Single-phase inverters convert DC power into AC power with a single-phase output. Widely used in residential and small-scale applications with lower power requirements, they are simpler and more affordable than three-phase inverters. However, their usage is limited due to their lower power output capabilities.
Three-Phase Inverters
Three-phase inverters convert DC power into three-phase AC power, primarily employed in industrial and commercial settings with higher power demands. Offering better efficiency and the ability to handle heavier loads than single-phase inverters, they are more complex and come with a higher price tag.
Inverter Batteries and Their Types
Inverter batteries are an essential component of any inverter system that relies on battery storage. They store the converted AC power from the inverter and supply it during power outages or when the solar energy system cannot generate sufficient power. There are different types of inverter batteries available, each with its own characteristics and suitability for specific applications.
Lead-acid batteries are the most common type of inverter batteries. They are affordable, readily available, and have been used for decades in various applications. However, they require regular maintenance, have a limited lifespan, and can be sensitive to extreme temperatures.
Lithium-ion batteries are a newer technology that offers several advantages over lead-acid batteries. They have a longer lifespan, require little to no maintenance, and are more compact and lightweight. Although lithium-ion batteries are more expensive upfront, they provide better long-term value due to their superior performance and durability.
When choosing an inverter battery, consider factors such as the battery capacity, the expected lifespan, the maintenance requirements, and the cost. It is also essential to ensure compatibility between the inverter and the battery to ensure optimal performance.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Inverter
Choosing the right inverter for your specific needs requires careful consideration of several factors. Here are some key factors to keep in mind when selecting an inverter:
- Power requirements: Determine the power capacity you need based on the appliances you want to power and their energy consumption.
- Efficiency: Look for inverters with high efficiency ratings to minimize energy losses during the conversion process.
- Voltage compatibility: Ensure that the inverter is compatible with the voltage requirements of your electrical appliances and power sources.
- Safety features: Consider inverters with built-in safety features such as overload protection, short circuit protection, and temperature monitoring.
- Warranty and support: Look for reputable brands that offer warranties and reliable customer support to address any issues that may arise.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision and choose an inverter that meets your specific power needs and budget.
Final Thoughts
Inverters are essential devices that enable us to utilise DC power from sources such as batteries or solar panels to power our homes, businesses, and various appliances. Understanding the different types of inverters and their applications is crucial for making the right choice based on your specific power requirements.
Whether you are looking for an off-grid inverter for your solar energy system, a grid-tied inverter to take advantage of net metering, or a stand-alone inverter for portable power, there is a wide range of options available. Consider factors such as power capacity, efficiency, safety features, and compatibility when selecting an inverter.
Furthermore, choosing the right inverter battery is equally important to ensure reliable backup power during outages or when solar energy generation is insufficient. Lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries are the two main types to consider, each with its own advantages and suitability for different applications.
By understanding the different types of inverters and considering the factors mentioned, you can confidently choose the right inverter system for your needs. Whether you want to harness solar energy or have a reliable backup power source, the right inverter will ensure uninterrupted power supply and peace of mind.
Remember, when it comes to inverters, making an informed decision is key to unlocking the full potential of your power sources.

SHOP INVERTERS TODAY